Introduction
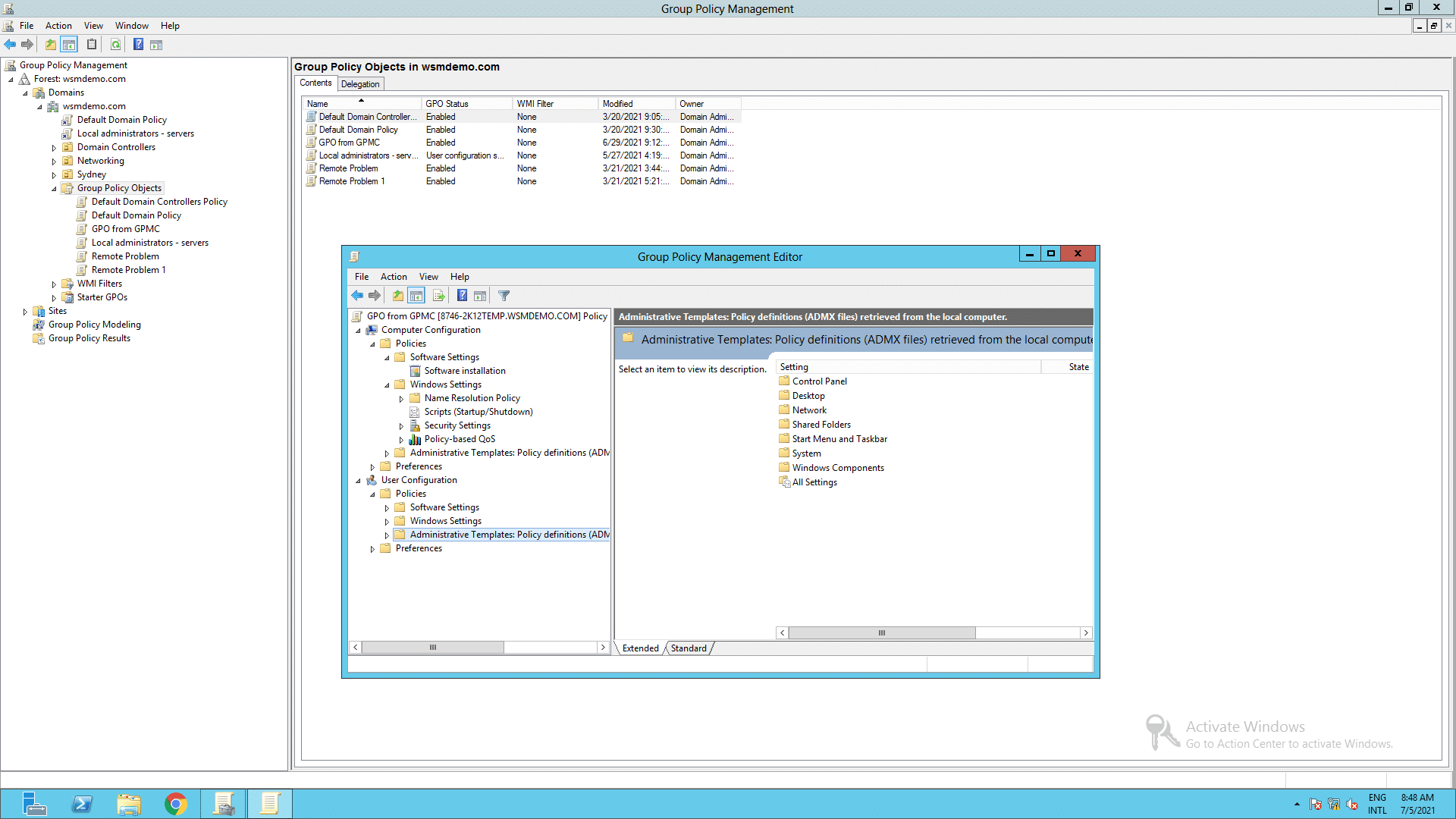
Group Policy includes policy settings that affect both users and computers. The settings under Computer Configuration control how the computer is configured. The settings under User Configuration control the user’s log-on session. Settings configured for a computer are processed first when the computer starts, followed by the user configuration settings when the user logs on.
Both Computer and User Configuration have the following settings:
1) Software Settings
2) Windows Settings
3) Administrative Templates
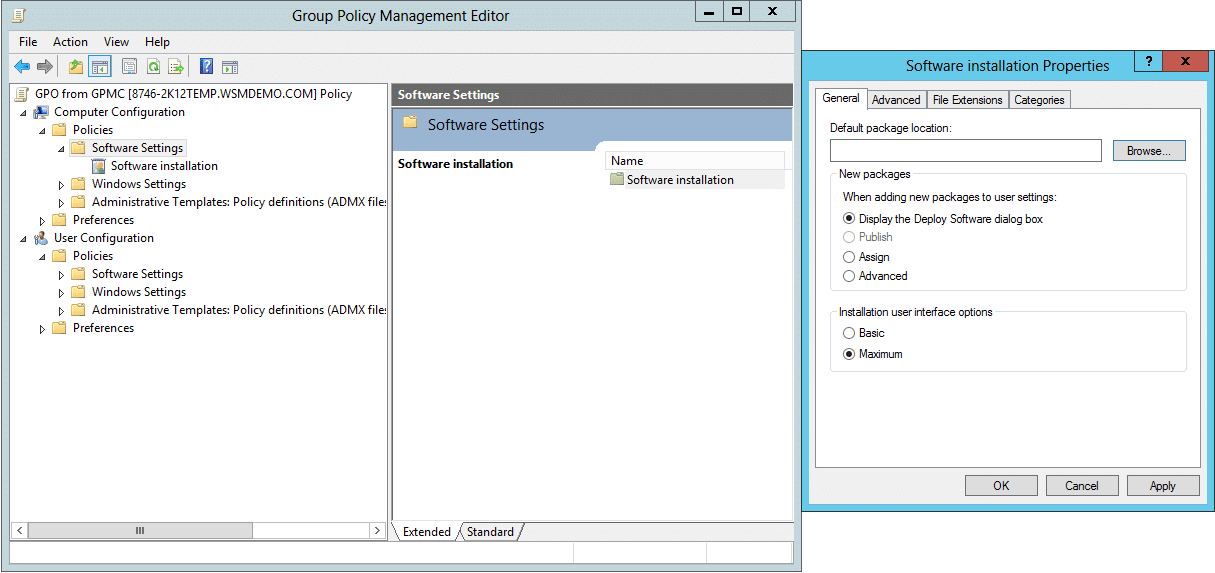
Software Settings
Software installation and upgrades are configured here. Two options are available for installing software.
1) Assign
When a software package is assigned to a computer, it is automatically installed on that computer and is available for use to all the users who log on to that computer. When a software package is assigned to a user, it is automatically installed when the user logs on to a computer and is available only for that user. The software assigned to a user will be available on all the machines the user logs on to.
2) Publish
The software can be published only to users and not computers. Published software is made available to the users in the Add/Remove Programs of the Control Panel. Users can install the software whenever the need arises.
Windows Settings
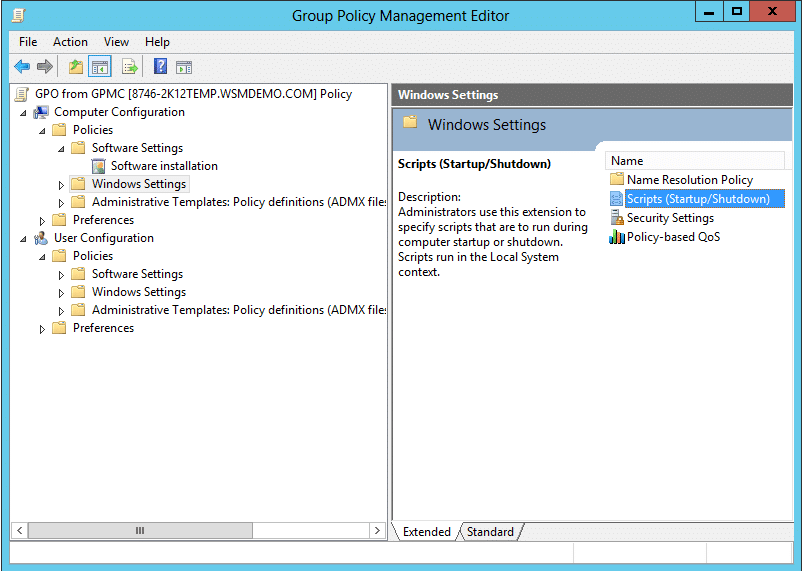
The following are some of the important Windows Settings that can be configured using Group Policies.
1) Scripts
Scripts are programming codes that perform some action when executed. Startup/Shutdown scripts can be configured for the computer and Logon/Logoff scripts can be configured for the user.
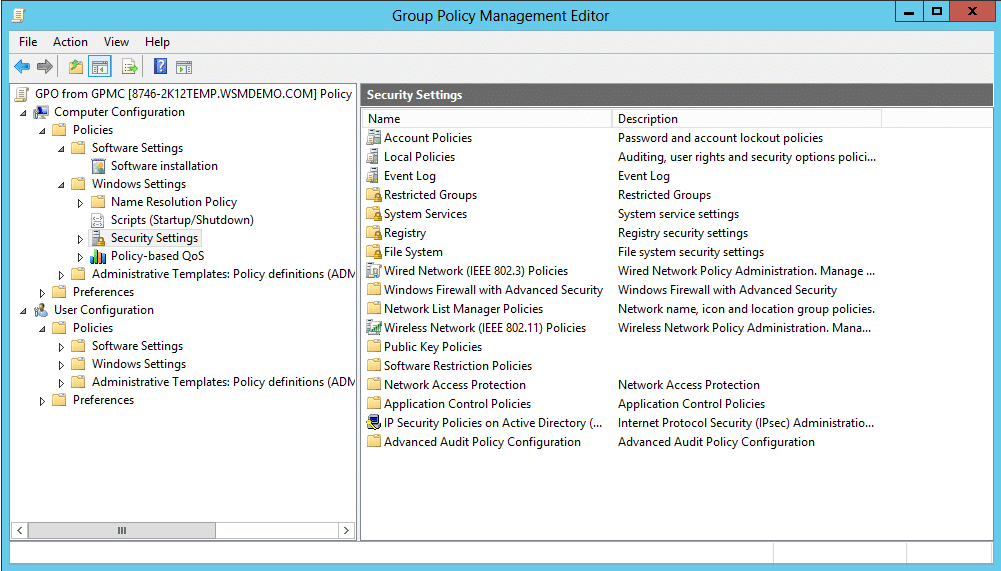
2) Security Settings
Both the Computer and User configuration sections have many important security settings that can be configured here. Some of the most important settings are mentioned below.
a) Account policies: Settings related to password complexity, password length, password age, account lockout, etc., can be configured here.
b) Local Policies: Local Policies include Audit Policy, User Rights Assignment, and Security Options.
c) Audit policy: Audit policy can record any successful or failed events which can be later viewed through an event log.
d) User Rights Assignment: Settings such as log on locally, log on through remote desktop services, etc., can be configured here
e) Security Options: It includes the settings for Interactive logon messages, user account control, etc.
f) Software Restriction Policies: Administrators can configure a Software Restriction Policy to determine what software a user can install on a machine. By creating Hash rules, Certificate rules, Path rules, etc., administrators can restrict users from installing harmful software.
g) Internet Explorer Maintenance: This setting can be used to impose organization-wide internet policy by configuring proxy servers, homepage, etc. This setting is available only under User configuration.
h) Folder Redirection: This setting enables the administrator to store important user files such as profile folder and home folder in a secure, centralized location such as a file server. It results in high availability of user’s files and folders and easier management of backup and restores. This setting is available only under user configuration.
Besides the above settings, there are other settings such as IP Security Policy, Public key policy, Windows Firewall, Registry and much more that can be configured under this section.
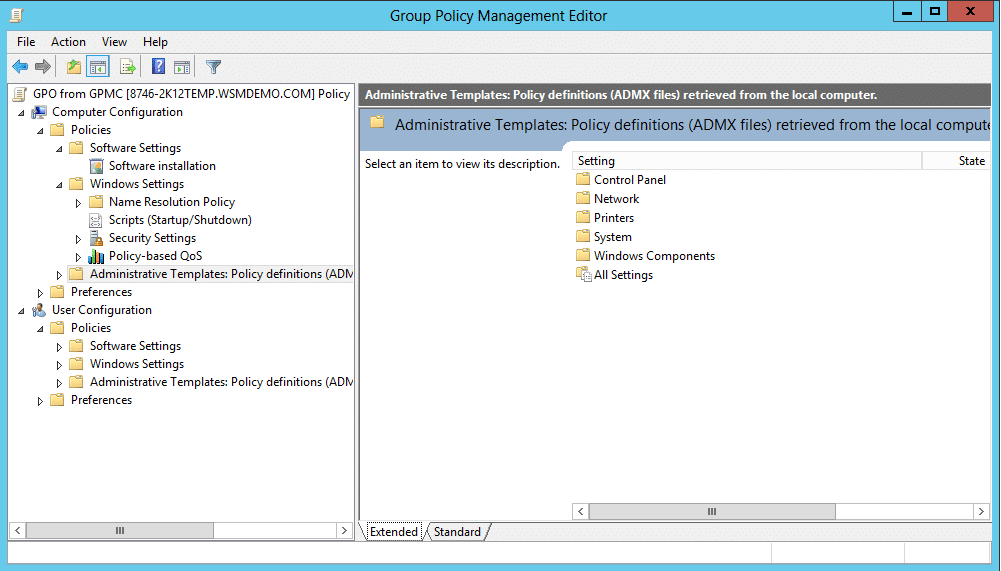
Administrative Templates
It contains a number of settings that can be used to customize the user/computer environment. Some of the important settings available under Computer Configuration are as follows:
1) Windows Components: Contains settings related to NetMeeting, Task Scheduler, Windows Installer, etc.
2) System: Contains settings related to Disk Quotas, Group Policy, Logon, Shutdown Options and much more.
3) Network: Contains settings related to Network Connections, Offline Files, etc.
Some of the important settings available under User Configuration are as follows:
1) Control Panel: Contains settings related to the management of Control Panel such as Remove Add/Remove Programs.
2) Desktop: Contains settings related to the management of the User’s Desktop such as Wallpaper settings, Show/Hide desktop icons, etc.
3) Start Menu and Taskbar: Contains settings related to the configuration of the start menu and taskbar such as lock taskbar, classic start menu, etc.
People also read
Managing GPOs in Active Directory


