What are Active Directory object attributes?
Active Directory (AD) object attributes are pieces of information or data that define the properties of the objects. For example, a computer object would have AD attributes such as computer name and DNS name. All AD attributes have an LDAP name that can be used in LDAP queries, such as displayname for ‘Full Name’, givenname for ‘First Name’, and mail for ‘Email Address’.
Each attribute would have unique values based on the resource in the AD network that the object represents. What object attributes an object should have is defined by what are known as object classes.
Object classes
All AD object attributes are created based on what is known as a schema. A schema is a database of templates that define objects and their AD attributes. Object classes are a part of the schema. There are three types of object classes that are arranged in hierarchical order. They are:
Abstract class: An abstract class is a top-level class that contains other abstract or structural classes. It defines only the basic attributes of an object.
Structural class: A structural class is the main component that defines an object and what attributes it should have. A structural class always comes under an abstract class or another structural class.
Auxiliary class: Auxiliary class contains additional attributes that the other classes can inherit from. These attributes are usually ones that the other classes do not want to define but can inherit whenever necessary. Auxiliary classes can be subclasses of an abstract class or other auxiliary classes.
You can learn more about schema and object classes here.
Viewing and modifying AD object attributes
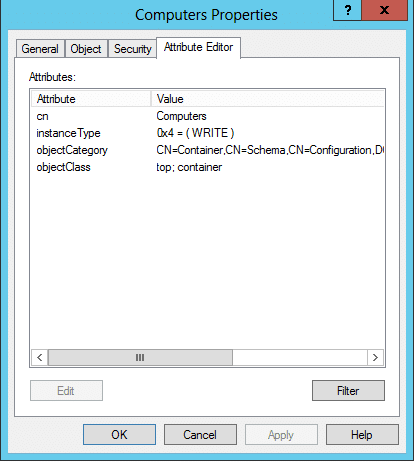
To view an AD object’s attribute, you can perform the following steps:
- Go to Start and open Administrative tools.
- Click on Active Directory users and Computers.
- Right click on the object whose attributes you wish to view, and click Properties.
- In the dialogue box that opens, you will be able to view all the AD attributes of the object categorized based on the attribute type.
- To modify the attributes, click on the Attribute Editor tab, and you will be able to see a list of all the attributes and their LDAP names.
- Click the Edit button to edit the attributes. You will have to have permissions to edit the attributes in order to perform this action.