Domain Functional Levels – An overview
Domain functional level (DFL) determines the features of a Domain Controller (DC) based on the Windows Server Operating System (OS) it runs on. A feature set of a particular DFL will be available for a DC if it runs on the operating system version that is compatible with the functional level. Note that, the OS version constraint is only for the domain controller and not applicable for the member servers or the workstations in the domain. Thus larger organizations need not worry about upgrading every single workstation in their network to the specific OS for availing features of a particular DFLs.
Choosing Domain Functional Level
When AD DS is deployed, you can choose the functional level of the forest. DFL should always be chosen at the same level or higher level than the Forest Functional Level (FFL). Further, by default, the DFL for any new domain added to the forest will take the same level as the FFL. For instance, if the FFL is Windows Server 2008, then the DFL can be set as the same or higher level. It’s highly recommended to always set the latest version of the Windows Server as the functional level. This helps in leveraging all the latest AD DS features that are available.
Prerequisites to raise the domain functional level
The process of raising the DFL is done to increase the capabilities and enhance the security of the domain. The Windows DFL has a new and upgraded set of features in every succeeding OS version. It is advisable to upgrade the functional level once the prerequisites are met.
- You must be part of the Domain Admins group to raise the DFL.
- If you’re raising the functional level of a domain, ensure that all the DCs in the domain is running OS version that is compatible with the new functional level.
Domain Functional Levels and their features
The following table lists the Windows Server version and its DFL features.
Things to keep in mind:
- Every iterative version of Windows server includes the feature set of the previous level plus the additional features.
- You cannot set the DFL to a level that is lower than the forest functional level.
- It is not possible to roll back to a lower level from Windows server R2 functional level. If a DFL has to be set beyond Windows 2008 R2, rebuilding the whole domain is the only option.
| Domain Functional Level | Available Features |
| Windows 2000 native | Universal groups for both distribution and security groups.Group nestingGroup conversion between security and distribution groups.Security identifier (SID) history |
| Windows Server 2003 | .NET technologies supportWindows XP integrationIncreased security and built-in firewall.Improved disk management.Provides a backup system to restore lost files.Internet Information Services (IIS) v6.0 |
| Windows Server 2008 | Last Interactive Logon InformationFine-grained password policiesPersonal Virtual DesktopsSupports Advanced Encryption for the validation in Kerberos protocol. |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | Active Directory Administrative CenterPowerShell 2.0Support for the .NET Framework in Server CoreEnhancements to authentication mechanism. Using this feature the information in the token can be extracted whenever a user attempts to access any of the claims-aware application that has been developed to determine authorization based on a user’s logon method.Live MigrationAutomatic Service Principal Name management. This feature is specifically for services running on a computer under the context of a Managed Service Account. |
| Windows Server 2012 | Improvements to reduce authentication failures due to large service tickets.User Access LoggingKDC resource group compression.Increase in the Kerberos Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) context token buffer size.Group Policy to set a maximum for the Kerberos SSPI context token buffer size.KDC with warning events for large Kerberos tickets.Windows Management InfrastructureSupport for claims, compound authentication, and Kerberos armoring. |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Software Inventory LoggingMobile Device Management RegistrationTiered Storage Spaces provides greater performance and scalabilitySite-to-site VPN Gateway |
How to check the Domain Functional Level
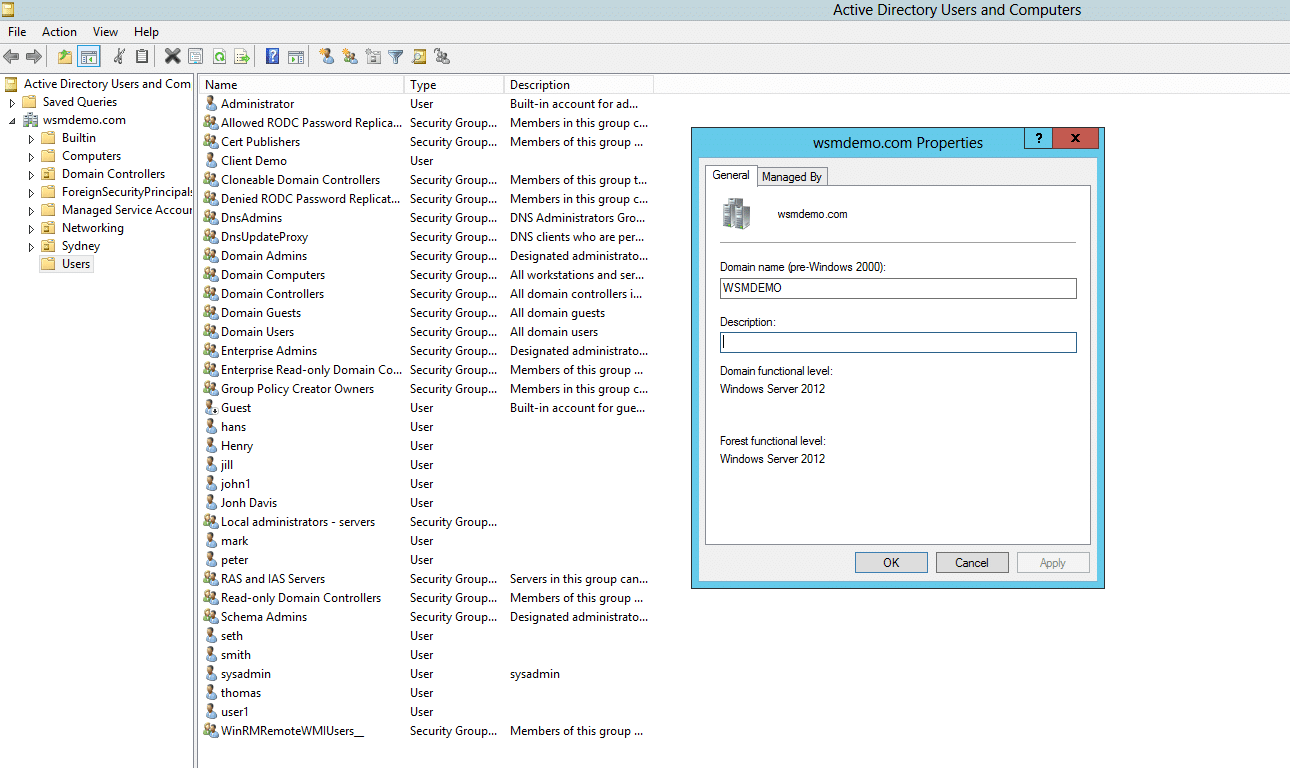
Before raising the domain functional level, it is necessary to check the existing domain functional level. Follow these steps:
- From the Server Manager panel, click on Tools and then select Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Right-click on the root domain from the pane on the left, and then click on Properties.
- The General tab displays the Domain and forest functional level.
Raising the Domain Functional Level
- From the Administrator Tools panel, select Active Directory Domains and Trust.
- Right-click the root domain for which you want to raise the domain functional level and select Raise Domain Functional Level.
- Select an available Domain Functional Level and then click on Raise.
- This raises the functional level of a domain.
Security impact of Domain Functional Levels
Each version of the Windows Server comes with a list of updates, and these updates bring major improvements on the security front. Hence, it is important to upgrade your domain functional level to the appropriate level that contains the necessary security functionalities for your organization. Here are some major security upgrades from each Windows Server version:
- Windows Server 2008: Fine-grained Password Policies.
- Windows Server 2012 R2: Restricted Admin mode for Remote Desktop Connection, LSA protection, and Protected Users Security Group.
- Windows Server 2016: Enhanced credential management functionalities.